
Oblique and anteriorposterior view Xrays of a normal foot showing... Download Scientific Diagram
A foot X-ray can assist your healthcare provider in determining the cause of any unexplained swelling, pain, or tenderness in your foot or ankle. After a broken ankle bone has been repaired, foot X-rays are frequently performed. Your doctor will be able to tell from the X-ray whether the bone was properly set.

Normal Foot X Ray Normal foot series Image Check you have the right
An approach to the traumatic foot x-ray. 1. Adequacy. This view is best used in the evaluation of midfoot and forefoot [5]. Lateral: should include projection of ankle in addition to foot [5]. The base of 1st, 2nd, and 3rd metatarsals should align with three cuneiform bones [5].
NORMAL FOOT 7
This review discusses causes of chronic foot pain (Table 1 2, 3; Figure 1), their clinical presentations, and their radiologic findings (Table 2 4), and explains the American College of Radiology.

EMRad Can’t Miss Adult Ankle and Foot Injuries In the Setting of Trauma
Description Toe and forefoot fractures often result from trauma or direct injury to the bone. Fractures can also develop after repetitive activity, rather than a single injury. This is called a "stress fracture." Fractures may either be: Non-displaced, where the bone is cracked but the ends of the bone are together

Xray left foot Fig. 4 Xray left foot Download Scientific Diagram
x-ray beam centered to the base of the 3 rd metatarsal the beam must be angled approximately 10° posteriorly towards the calcaneum to mimic the arch of the foot, this may change if the arch is high or flat collimation lateral to the skin margins anterior to the skin margins of the distal phalanges posterior to the skin margins of the calcaneum
Normal foot xrays Image
Conclusion

Oblique radiograph of the left foot with the clearly visible additional... Download Scientific
Indications This view is useful in the assessment for joint abnormalities, determining the degree of dorsal or plantar displacement in fractured bones, soft tissue effusions or gas (i.e. osteomyelitis) and in locating opaque foreign bodies. Patient position the patient may be supine or upright depending on comfort

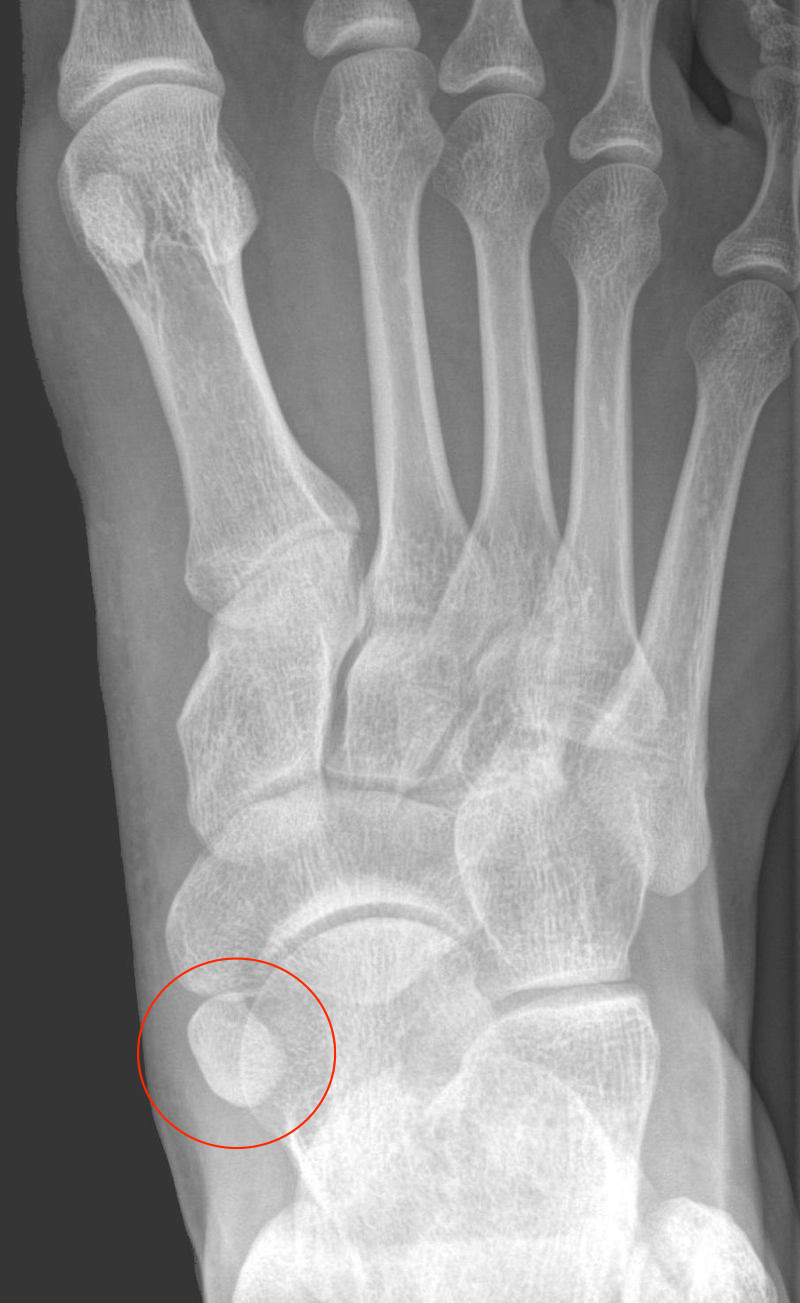
Bipartite hallux sesamoid Image
The normal radiograph of the left foot is from a 53-year-old female. The foot is shown in the AP (A), oblique (B), and lateral projections (C). AP: anterior-posterior. Graphic 85820 Version 2.0. Company. About Us Editorial Policy Testimonials Wolters Kluwer.

Normal Foot X Ray Normal foot series Image Check you have the right
Objective. The purpose of this article is to discuss the radiographic assessment of pediatric foot alignment. Clinical scenarios are included to orient the learner to the evaluation of pediatric foot alignment. Abnormalities discussed include, but are not limited to, talipes equinovarus (congenital clubfoot), planovalgus, and vertical talus.
Foot xrays Don't the Bubbles
This book chapter provides a comprehensive overview of the normal anatomy and biomechanics of the foot and ankle, as well as the radiographic techniques and measurements used to evaluate them. It includes detailed illustrations and tables to help readers understand the normal variations and ranges of motion of the foot and ankle joints. The chapter also offers a link to full text access for.

Normal ankle xray netlaser
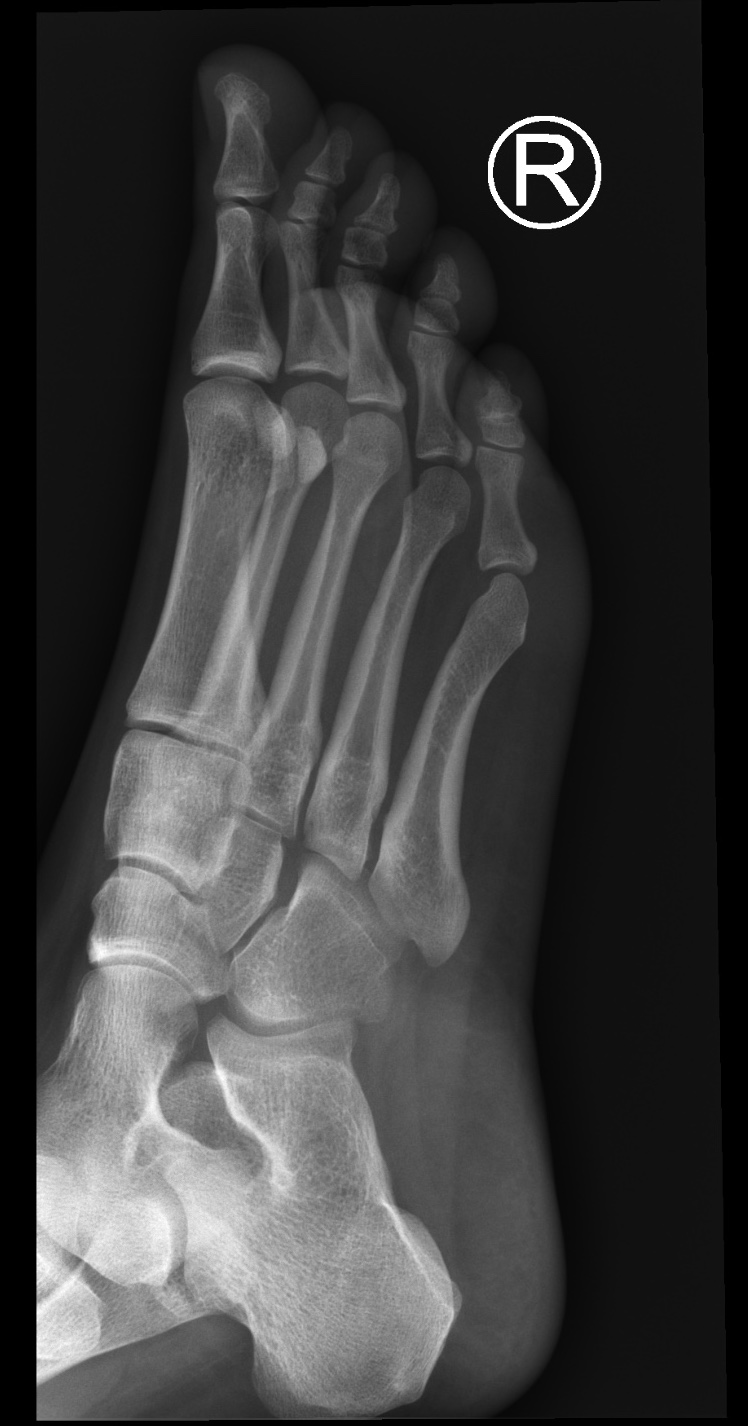
Overview What is a foot X-ray? A foot X-ray is a test that creates a black-and-white picture of the inside of your foot. The image displays the soft tissues and bones of your foot. These bones include your ankle bones (tarsal bones), the front end of your foot (metatarsal bones) and your toes (phalanges).

Normal ankle series Image
Introduction » 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 » Conclusion Tutorial introduction Hip fracture Femoral shaft Knee Tibia and fibula Ankle Tutorial conclusion Login Register « Previous Tutorials Next » Trauma X-ray - Lower limb Foot Key points Carefully check the cortical edge of all bones on all views available
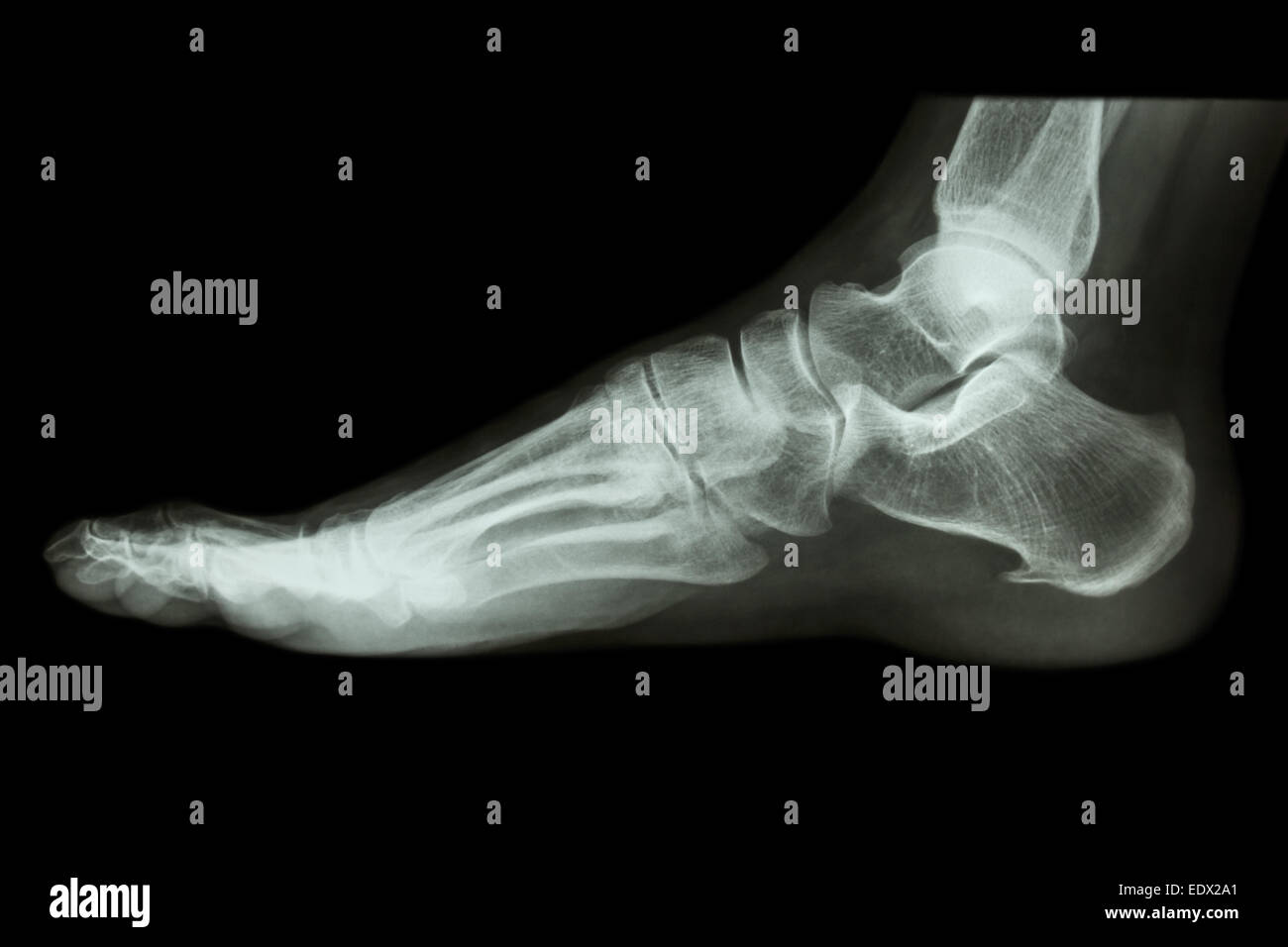
Xray normal human's foot lateral Stock Photo Alamy
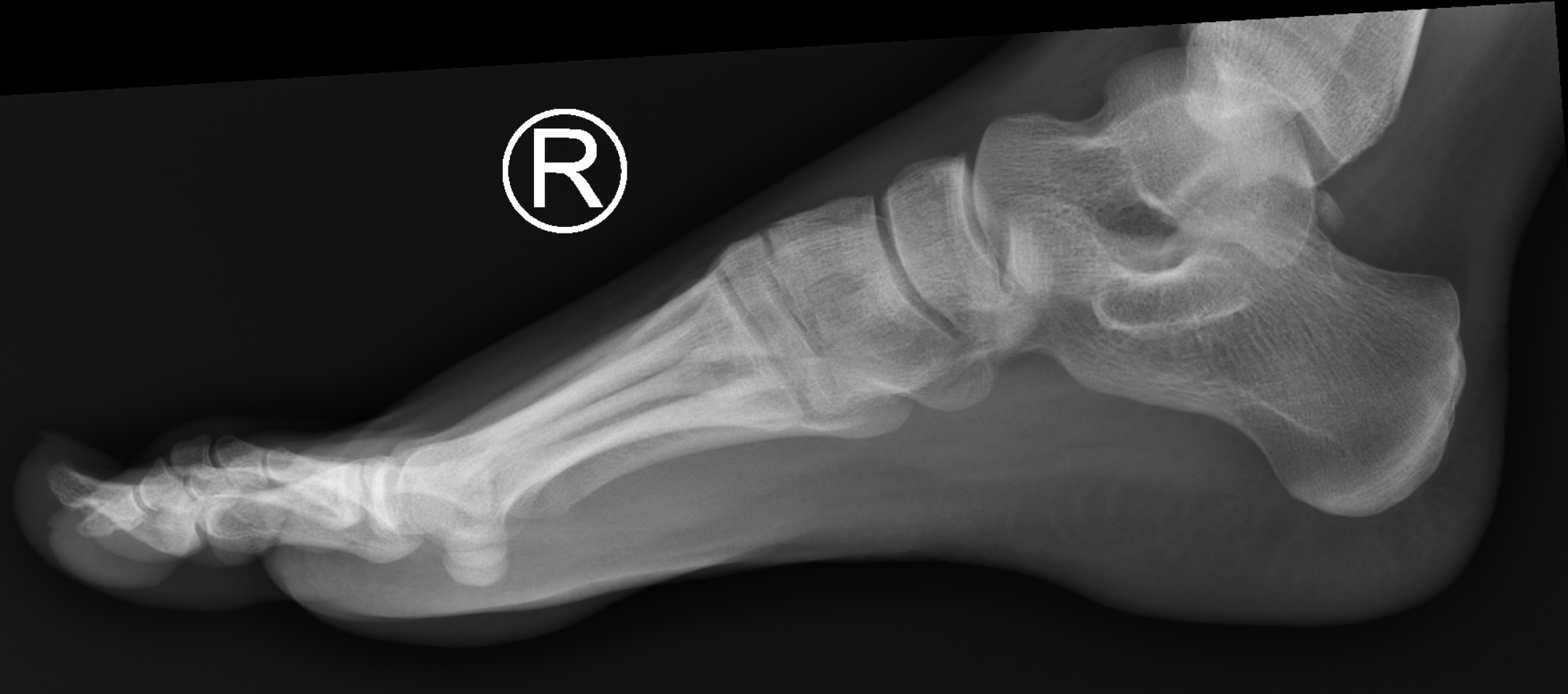
Pain. ?fracture Patient Data Age: 20 years. Gender: Female x-ray Frontal Oblique Lateral Normal right foot radiographs in a young adult female for reference. Case Discussion Normal right foot radiographs in a young adult female for reference. 1 article features images from this case 11 public playlists include this case
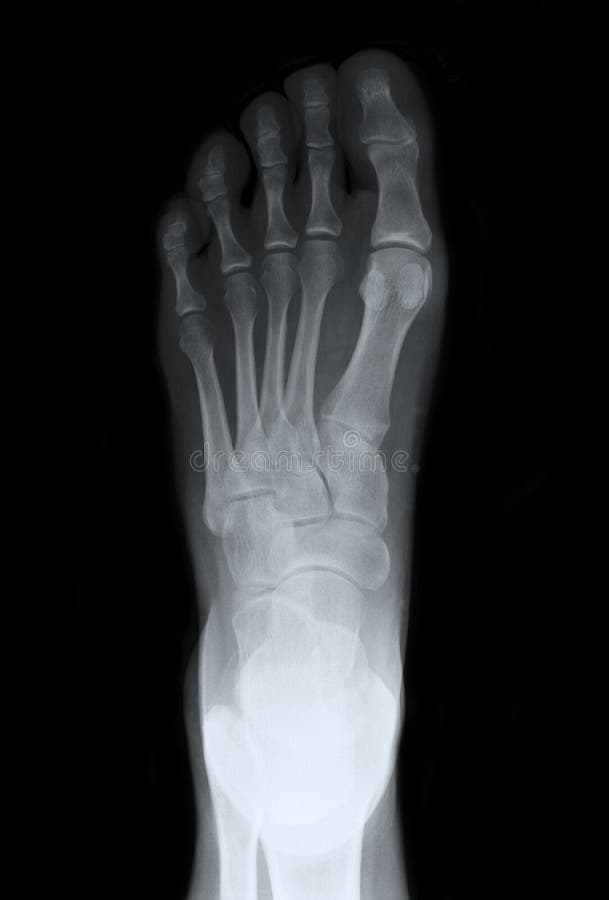
Left Foot Top Xray stock photo. Image of office, bones 23546186
Overview Along with questions of your medical history, your doctor may need to take x-rays of your foot to help aid in making a diagnosis to determine the cause of your foot pain. If the foot is broken it will be put into a cast. Toes that are broken are taped.

Image
Reference article This is a summary article. For more information, you can read a more in-depth reference article: foot series. Summary indications foot trauma with suspicion of bony injury foreign body examination procedure DP and oblique views of the foot not performed weight bearing in trauma DP (dorsoplantar)

Initial foot Xrays (AP and lateral views), exhibiting normal appearances. Download Scientific
Routine Radiographs. These include a series of ankle and foot X-rays. Fig. 2.1 (A and B) (A) Anteroposterior (AP) and (B) Lateral (LAT) views of ankle. • Oblique (mortise) views: Mortise view is 15-degree internal rotation view, which clearly shows ankle mortise in its true plane.