Convection in the Sun Science News
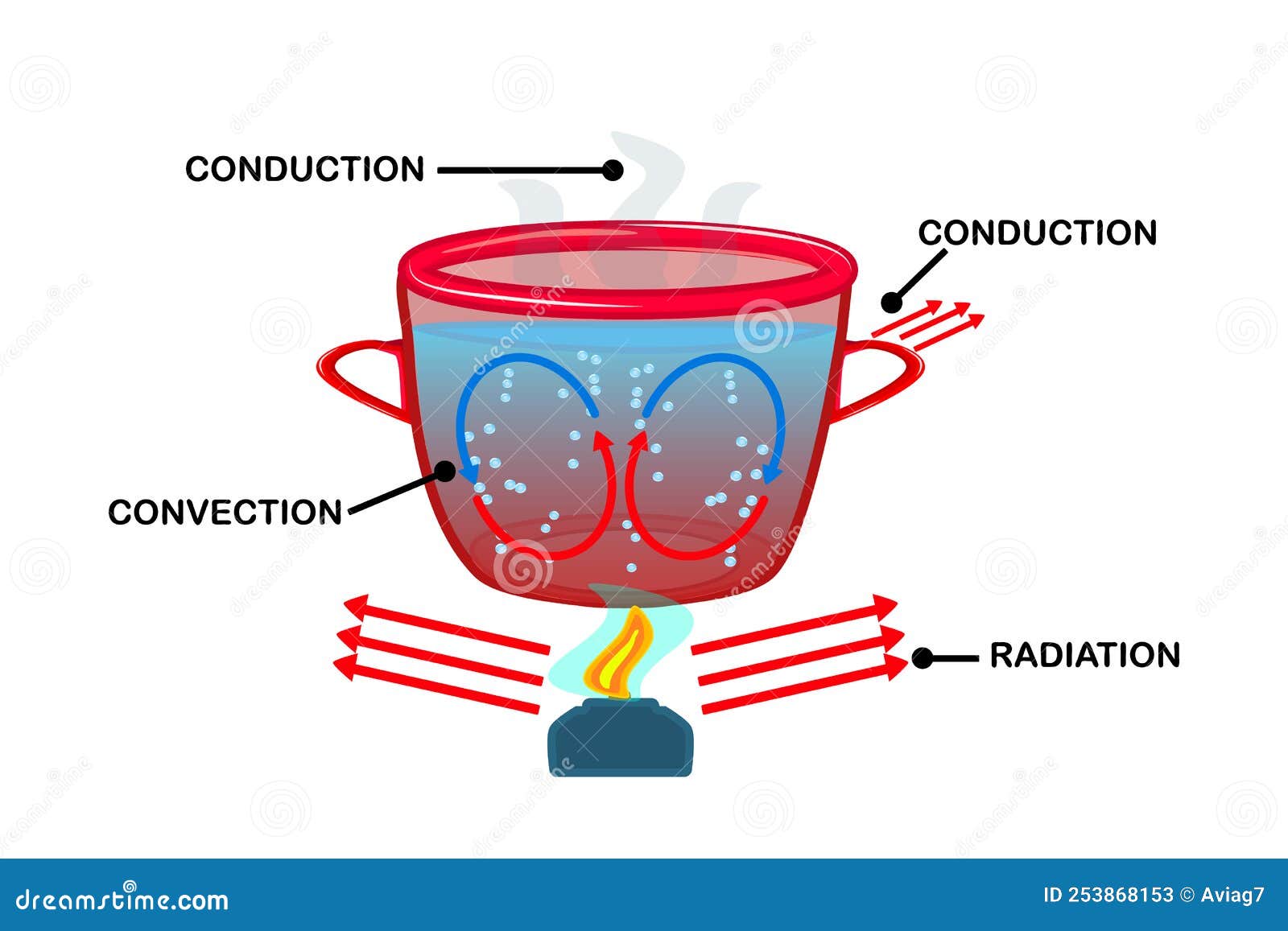
AboutTranscript. There are three forms of thermal energy transfer: conduction, convection, and radiation. Conduction involves molecules transferring kinetic energy to one another through collisions. Convection occurs when hot air rises, allowing cooler air to come in and be heated. Thermal radiation happens when accelerated charged particles.

How Do Convection Currents Work Inside The Earth CONVEKTION CDE
Where convection currents close convection current Movement within the earth's mantle caused by the heat of the core. move plates apart, constructive plate boundaries (margins) are formed.

Convection
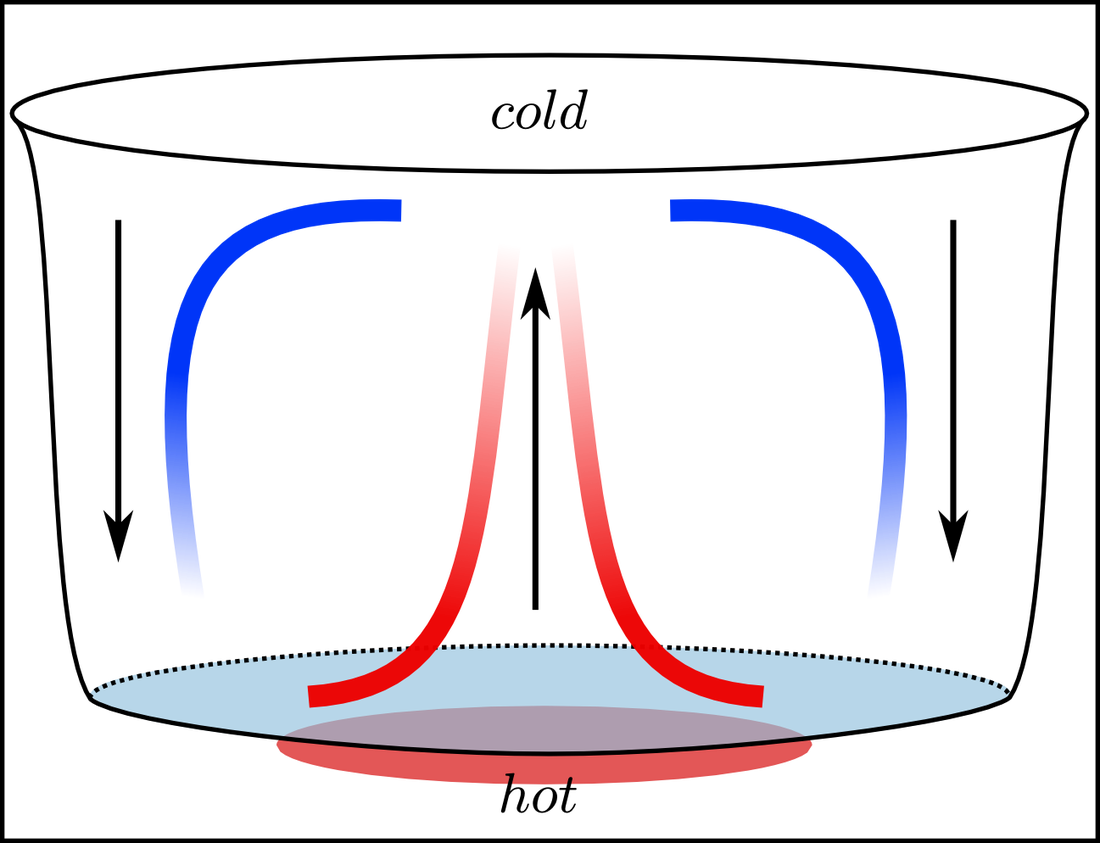
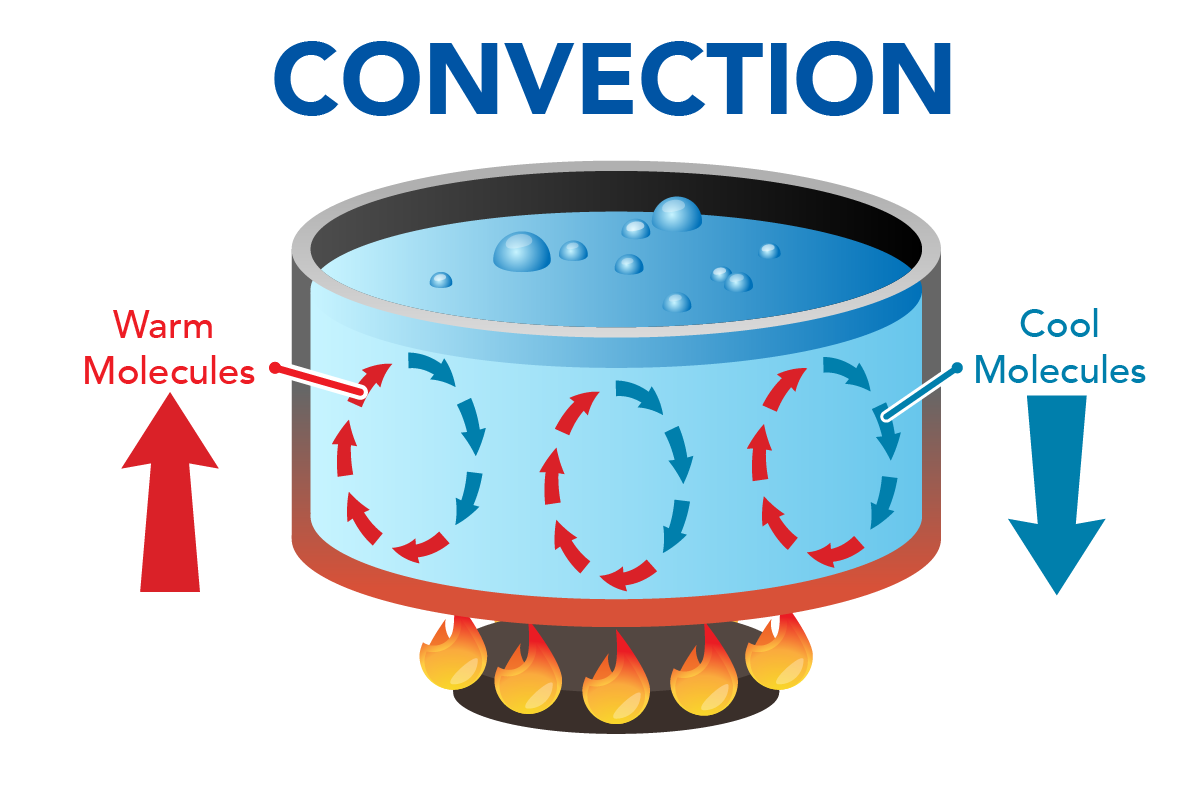
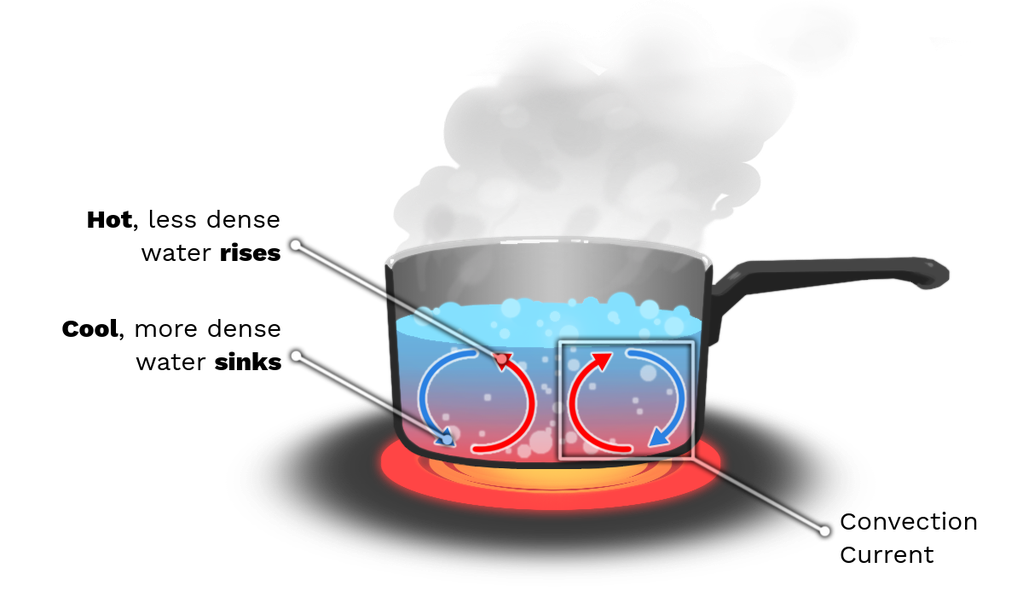
Convection Currents Made Easy. When part of a liquid or gas is heated, it expands and becomes less dense. The warmer, less dense liquid rises upwards, and the cooler liquid falls to take its place. This cycle of a liquid or gas rising and falling is called a convection current. We set up a very simple convection current demonstration using hot.

Convection
Yes, the Atlantic ocean is getting bigger and the pacific ocean is getting smaller due to the continental drift. This is caused by the natural moments of the plates as they glide on the semi-liquid mantle. This mantle often has currents caused by the subducting fluid and this force pushed the plates in many directions.
Describe the Formation of Convection Currents in the Mantle
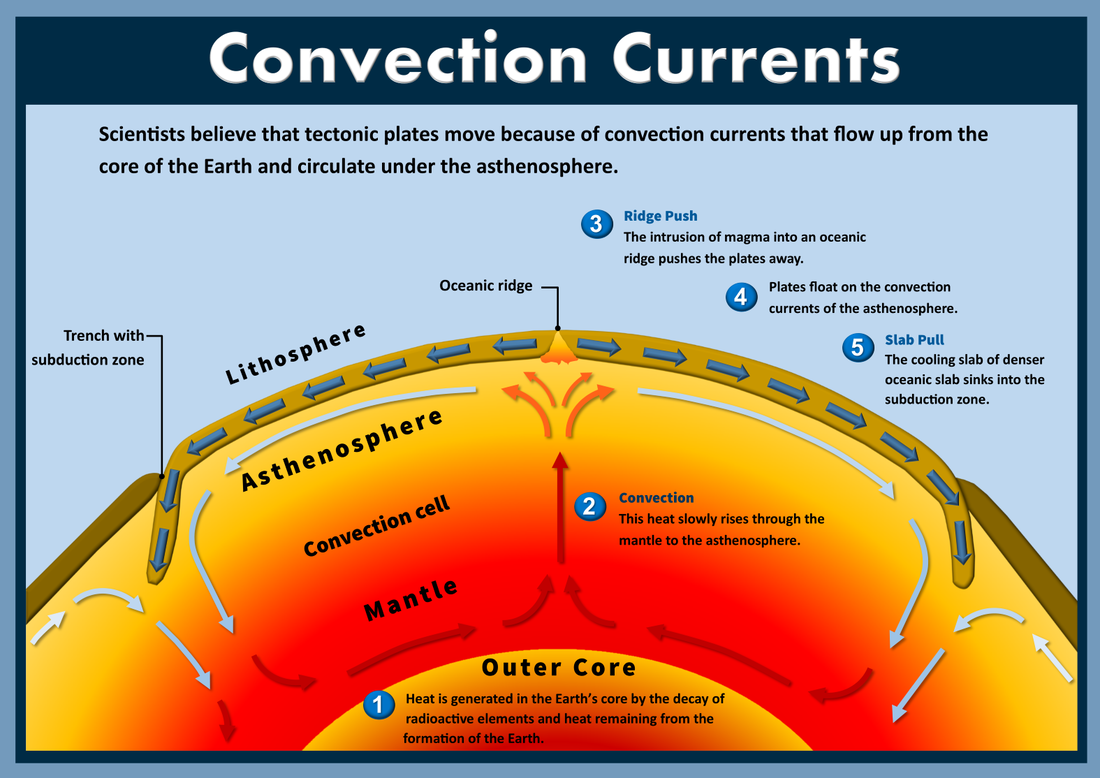
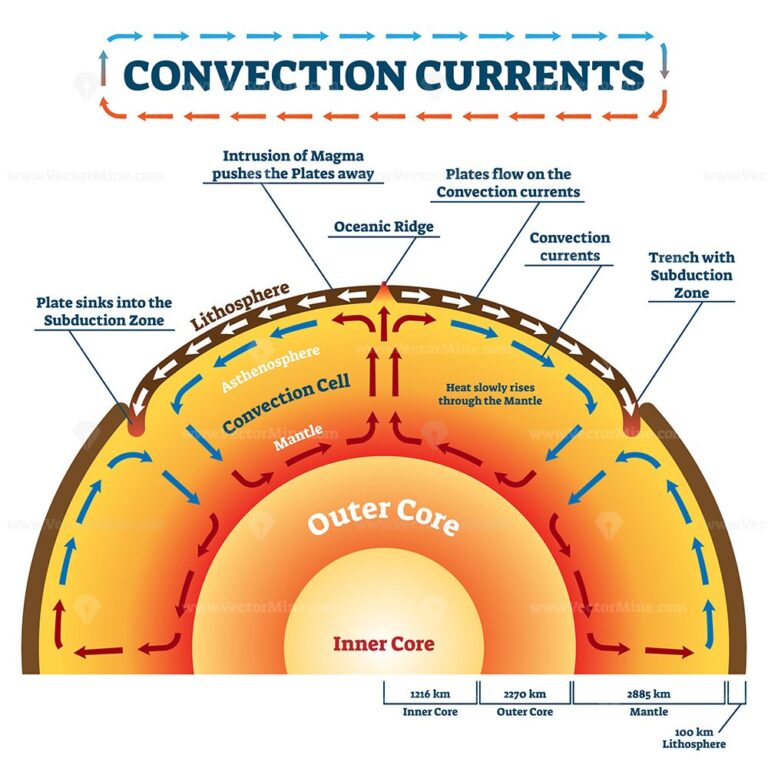
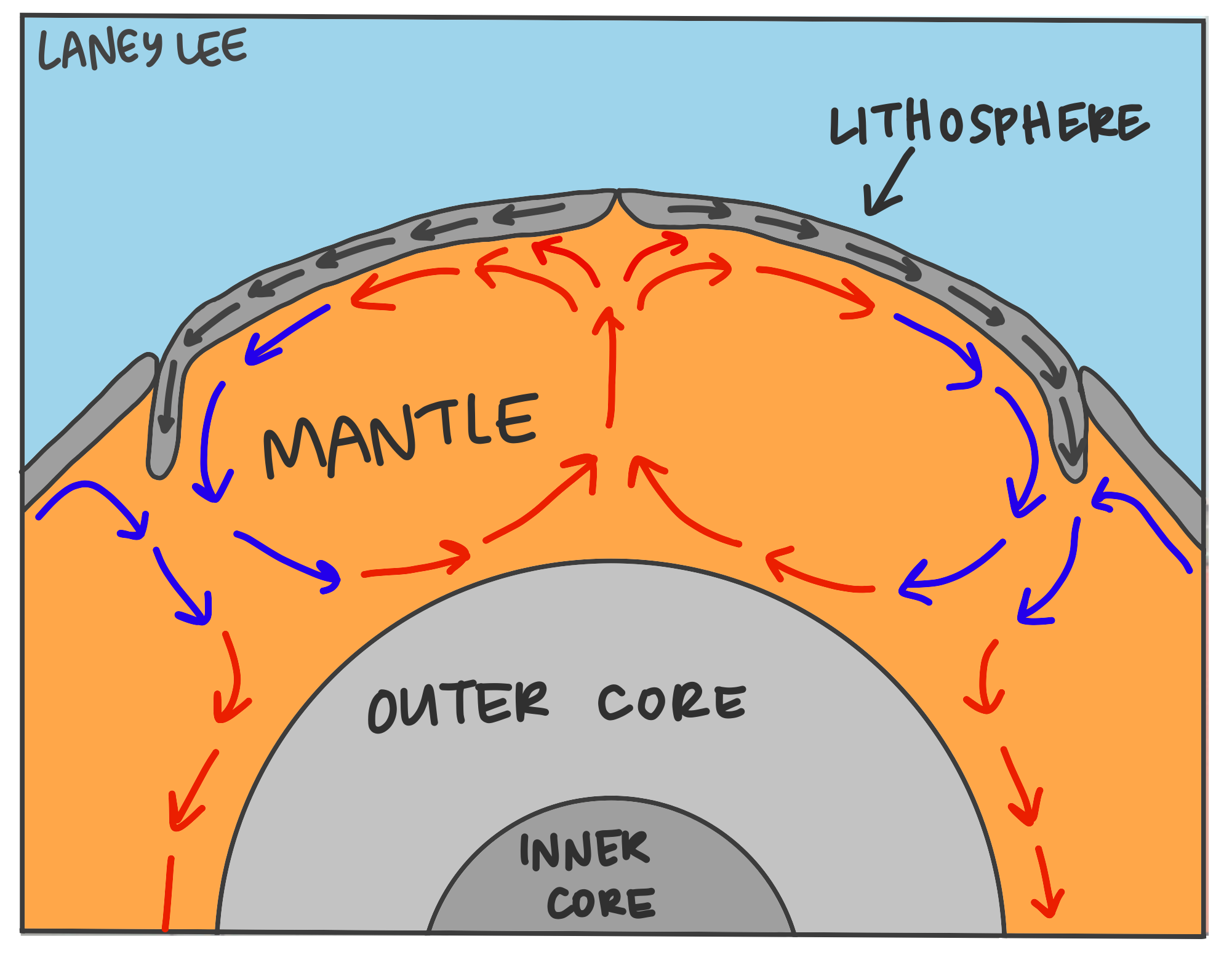
The common, simplified explanation for why tectonic plates are moving is that they're carried along on currents in the upper mantle, the slowly flowing layer of rock just below the Earth's crust. Converging currents drive plates into each other. Diverging currents pull them apart. This is mostly true. Hot mantle rock rises from the core and.
Convection Currents vector illustration VectorMine
Term. Convection currents. Definition. The movement caused within a fluid by hotter and therefore less dense material to rise, and colder, denser material to sink under the influence of gravity. + 1 more side. Term. The core. Definition. The centre of the Earth that is super heated and made of solid iron and nickel.
Introduction to heat transfer (2022)
Mantle convection is the main way heat from Earth's interior is transported to its surface, and this heat escapes principally through mid-ocean ridges. In fact, the connected mid-ocean ridge system is in essence a 80,000 km long volcano. Escaping heat along these ridges causes hot water to circulate through the crust in a "hydrothermal.
Atmospheric Sciences A simple model of convection to study the atmospheric surface layer
Convection Currents, and these are very important for studying weather. 3. Radiation: Heat transfer by IR radiation. How heat is transferred through space; also works well in gases. Example: the heat from the sun. > A hot object will give off IR radiation; the hotter it is, the more intense the radiation (e.g., a bonfire vs. a match). We can.
Convection the process Labster Theory
ATEP ©2008 UAF Geophysical Institute B-4 Convection Current Grades 5-8 T S UNAMI Overview: During this lesson students observe convection currents by perform-. of the beaker, where they remained, fluttering gently on the current. diagram 1: no Heat Source diagram 2: Active Heat Source Convection Current Student Worksheet (page 2 of 3)

A Convection Current Created During The Day CONVEKTION CGR
Convection currents enable hot air balloons to rise, and also explain why it is often hotter in houses upstairs rather than downstairs. Most of our winds are caused by convection currents.
Convection Currents & Plate Tectonics Laney Lee
2. Thunderstorm: A thunderstorm can be the best example of convection currents. The warm water in the air rises upwards and turns into saturated water drops which form the clouds. In this process, the smaller clouds run into each other and hence the bigger clouds are formed.
Convection Key Stage Wiki
By Herb Kirchhoff. Convection currents transfer heat from one place to another by mass motion of a fluid such as water, air or molten rock. The heat transfer function of convection currents drives the earth's ocean currents, atmospheric weather and geology. Convection is different from conduction, which is a transfer of heat between.
Heat Transfer. Convection Currents Labeled Diagram. Stock Vector Illustration of methods
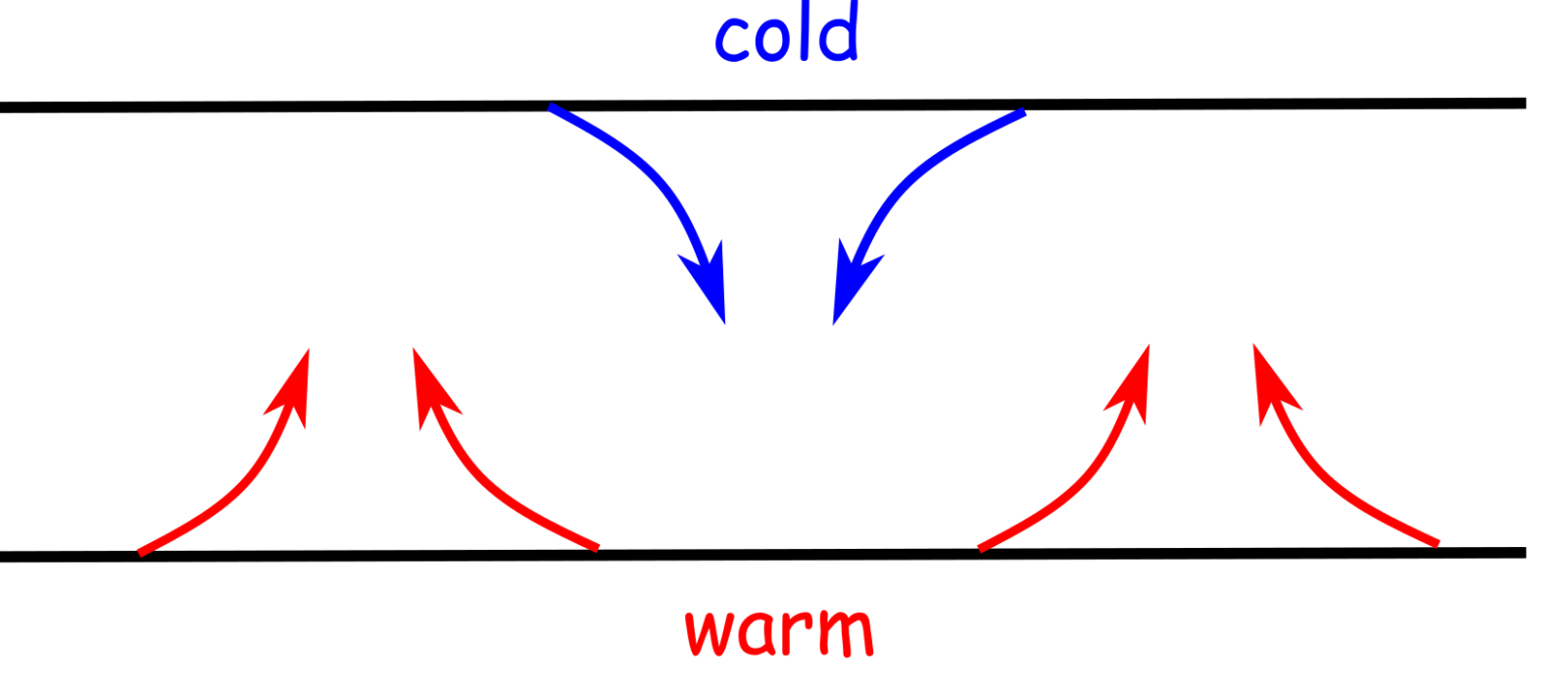
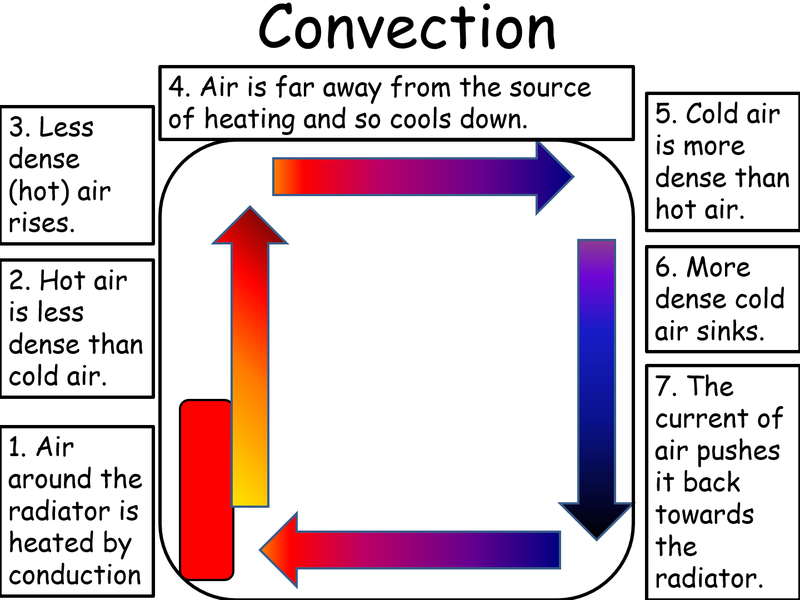
convection, process by which heat is transferred by movement of a heated fluid such as air or water.. Natural convection results from the tendency of most fluids to expand when heated—i.e., to become less dense and to rise as a result of the increased buoyancy.Circulation caused by this effect accounts for the uniform heating of water in a kettle or air in a heated room: the heated molecules.

Convection current the circular current of air caused by difference in air density resulting
Convection currents, that occur within the molten rock in the mantle, act like a conveyor belt for the plates. Tectonic plates move in different directions. The direction of movement and type of plate margin is determined by which way the convection currents are flowing. Convection currents. The heat from the core is transferred to the mantle.

Convection currents Diagram Quizlet
Examples of Convection Currents. Let us discuss a few examples of a convection current. Campfires: The convection currents heat our hands.That's why we feel hot around the campfire. Convection currents are present in the air: A typical example of a convection current is the warm air that rises towards the ceiling of a house since the warm air is less dense than the cold air.

Types of Heat Transfer Convection
Examples of convection currents can be observed in a pot of soup heating on the stovetop, the movement of molten material in the mantle of Earth, and the creation of a sea breeze. In each of these.